Latest updates on country situation
07 October 2024
Heavy and recurrent torrential rains since July 2024 have continued to cause floods in Cameroon’s Far North region. Until 3 October, the floods had affected around 365,000 people, with almost all residing in around 56,000 damaged or destroyed houses; damaged around 260 schools and 65 health centres; and flooded around 82,500 hectares of farmland. The departments of Mayo-Danay and Logone et Chari are the most affected. Urgent humanitarian needs include shelter, essential household items, food, WASH kits, and healthcare support, particularly psychosocial support. Poor road conditions are hindering humanitarian assistance. For the rest of the year, floods are estimated to affect a further 100,000 people in Far North region. (OCHA 05/10/2024, UNICEF 07/10/2024, WFP 08/10/2024)
10 September 2024
Since July 2024, Cameroon’s Far North region has been experiencing heavy rains that have caused floods and material damage in the departments of Diamaré, Logone et Chari, Mayo-Danay, Mayo-Kani, and Mayo-Tsanaga. Until 10 September, the impact hit at least 200,000 people, killing 11, including four children. The rains have also destroyed or damaged over 12,500 houses, inundated 30 schools and 16 health centres, destroyed close to 7,900 hectares of crops, and killed almost 1,300 livestock. These have aggravated the humanitarian situation in the region, which hosted 453,000 IDPs and 128,000 refugees until 31 August. Priority needs include food, shelter, NFIs, WASH access, and health services. (OCHA 10/09/2024, UNICEF 06/09/2024, ECHO 05/09/2024)
07 February 2024
On 5 February 2024, IOM released the Emergency Tracking Tool covering population movements in the department of Mayo-Tsanaga (Cameroon) for the 29 January to 5 February period. Insecurity following a series of non-state armed group attacks and looting incidents displaced over 3,700 people. They were displaced from Batawaya, Dingding, Ldamang, Ldubam-Bas, Magoumaz, Moskota, Oulad, Oupai, Tourou, and Ziver and relocated mainly to Ldamtsai-Carrefour Daugai, Ouro-Tada, Ségoulé Centre, and Yoborga Centre. (IOM 05/02/2024)
current crises
in
Cameroon
These crises have been identified through the INFORM Severity Index, a tool for measuring and comparing the severity of humanitarian crises globally.
CMR001 - Multiple crises
Last updated 30/11/2025
Drivers
Conflict/ Violence
Floods
International Displacement
Crisis level
Country
Severity level
4 High
Access constraints
3.0
CMR002 - Conflict in Far North region
Last updated 30/11/2025
Drivers
Conflict/ Violence
Crisis level
Country
Severity level
3.7 High
Access constraints
2.0
CMR003 - Anglophone crisis
Last updated 30/11/2025
Drivers
Conflict/ Violence
Crisis level
Country
Severity level
3.5 High
Access constraints
3.0
CMR004 - Displacement from CAR
Last updated 30/11/2025
Drivers
International Displacement
Crisis level
Country
Severity level
2.7 Medium
Access constraints
1.0
Analysis products
on
Cameroon
29 June 2023
Cameroon: Increase in cholera cases
DOCUMENT / PDF / 204 KB
Cameroon has been experiencing a cholera outbreak since October 2021. Although the number of reported cases was relatively low between late November 2022 and March 2023, there has been a significant increase since 27 March, particularly in Centre region, making it the new epicentre of the epidemic. The epidemic has since mostly affected Centre, Littoral, South, and West regions, with new cases reported in 29 out of 58 districts countrywide.
17 August 2022
Lake Chad Basin: Impact of extreme weather & climate events on food security
DOCUMENT / PDF / 1 MB
This report aims to explore the impact of extreme weather and climate events on the humanitarian situation in the Lake Chad Basin. Since the 1970s in West and Central Africa, river floods and agricultural and ecological droughts have been increasing while average rainfall has been decreasing. These phenomena have an impact on availability of resources and land, and consequently on the economic and living conditions of the regions’ populations.
19 February 2021
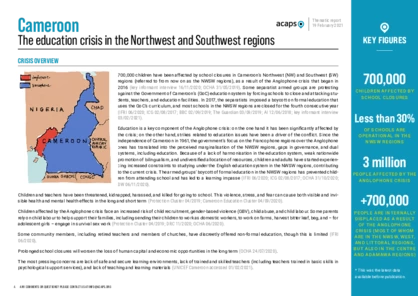
Cameroon: Education crisis in North West and South West regions
DOCUMENT / PDF / 2 MB
This report consolidates information from a wide range of available secondary data sources on the Anglophone crisis in Cameroon, including UN agencies, NGOs, the World Bank, media, and key informant interviews conducted in November 2020 and February 2021. Prior to publication, the report was shared with external partners working in Cameroon to cross-check information.
Attached resources
30 March 2020
Cameroon: COVID-19 outbreak
DOCUMENT / PDF / 389 KB
Cameroon has 54 confirmed cases of COVID-19 in Central Region, Littoral Region and West Region as of 23 March 2020. Cameroon’s Ministry of Public Health has developed a preparedness plan for COVID-19, including active surveillance at points of entry, in-country diagnostic capacity at the national reference laboratory, and designated isolation and treatment centres.
21 January 2020
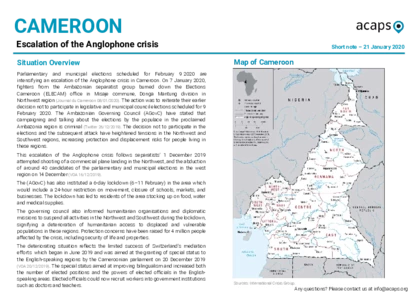
Cameroon: Escalation of the Anglophone crisis
DOCUMENT / PDF / 380 KB
Parliamentary and municipal elections scheduled for 9 February 2020 are intensifying an escalation of the Anglophone crisis in Cameroon. On 7 January 2020, fighters from the Ambazonian separatist group burned down the Elections Cameroon office in Misaje commune, Donga Mantung division in Northwest region. The action was to reiterate their earlier decision not to participate in legislative and municipal council elections scheduled for 9 February 2020.