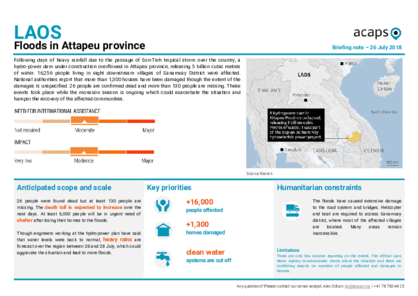
Laos is vulnerable to climate hazards, especially floods and storms. Because of poor socioeconomic conditions, the country’s capacity to adapt to climate change is low. In early August 2023, heavy rains caused flooding and triggered landslides that resulted in casualties (including at least six deaths) and infrastructure damage.
The flooding affected 550 villages across 50 districts in the 12 provinces of Bokeo, Bolikhamxai, Champasak, Houaphan, Khammouan, Luang Prabang, Savannakhet, Vientiane, Vientiane Capital, Xaignabouli, Xaisomboun, and Xiangkhouang. The most affected provinces were Bolikhamxai and Khammouan.
The flooding and landslides damaged around 155 roads, 80 irrigations systems, ten schools, three district hospitals, 225 toilets, 12 electric poles, and 310 vehicles in the affected provinces, as well as 471,000 acres of agricultural crops and around 105 barns used for rice storage, and killed nearly 18,800 livestock.
The disaster affected more than 110,000 people, including around 21,200 who are in urgent need of humanitarian assistance. The main humanitarian needs are food, potable water, basic hygiene items, livelihood, health, and WASH.
(WB accessed 30/10/2023, ECHO 10/08/2023, IFRC 18/09/2023)
Laos is vulnerable to climate hazards, especially floods and storms. Because of poor socioeconomic conditions, the country’s capacity to adapt to climate change is low. In early August 2023, heavy rains caused flooding and triggered landslides that resulted in casualties (including at least six deaths) and infrastructure damage.
The flooding affected 550 villages across 50 districts in the 12 provinces of Bokeo, Bolikhamxai, Champasak, Houaphan, Khammouan, Luang Prabang, Savannakhet, Vientiane, Vientiane Capital, Xaignabouli, Xaisomboun, and Xiangkhouang. The most affected provinces were Bolikhamxai and Khammouan.
The flooding and landslides damaged around 155 roads, 80 irrigations systems, ten schools, three district hospitals, 225 toilets, 12 electric poles, and 310 vehicles in the affected provinces, as well as 471,000 acres of agricultural crops and around 105 barns used for rice storage, and killed nearly 18,800 livestock.
The disaster affected more than 110,000 people, including around 21,200 who are in urgent need of humanitarian assistance. The main humanitarian needs are food, potable water, basic hygiene items, livelihood, health, and WASH.
(WB accessed 30/10/2023, ECHO 10/08/2023, IFRC 18/09/2023)